
What Are Receding Gums?
Gum recession is the process in which the tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls away from a tooth, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This condition is sometimes called gingival recession. It may start to seem like your teeth are getting longer. This can cause damage to the supporting bone. Many people don’t even notice that their gums have receded because it is a gradual process. However, over time, an exposed tooth root can not only look unsightly, but can cause tooth sensitivity, especially when eating cold or hot foods. Eventually, gum recession, if not treated, can cause tooth loss. Gum recession should not be ignored as it is an indication of serious underlying gum disease and possible an unstable bite.
Why Do Gums Recede
What causes receding gums in most people? There are a handful of reasons, including gum disease, forceful brushing, injury or teeth clenching and grinding. The surrounding bone structure may become damaged, and you may even lose some of your teeth if you do not get proper treatment. This disease can occur gradually, so you may not know you have it right away.
Gum recession is a major concern for many of our patients due to the poor esthetics and the possibility of sensitivity and decay. Studies have shown that 50% of people between 18-64 years of age have one or more sites with recession and 23.8 million people have one or more tooth surfaces with greater than or equal to 3 mm of gingival recession. It may affect one tooth or multiple teeth.
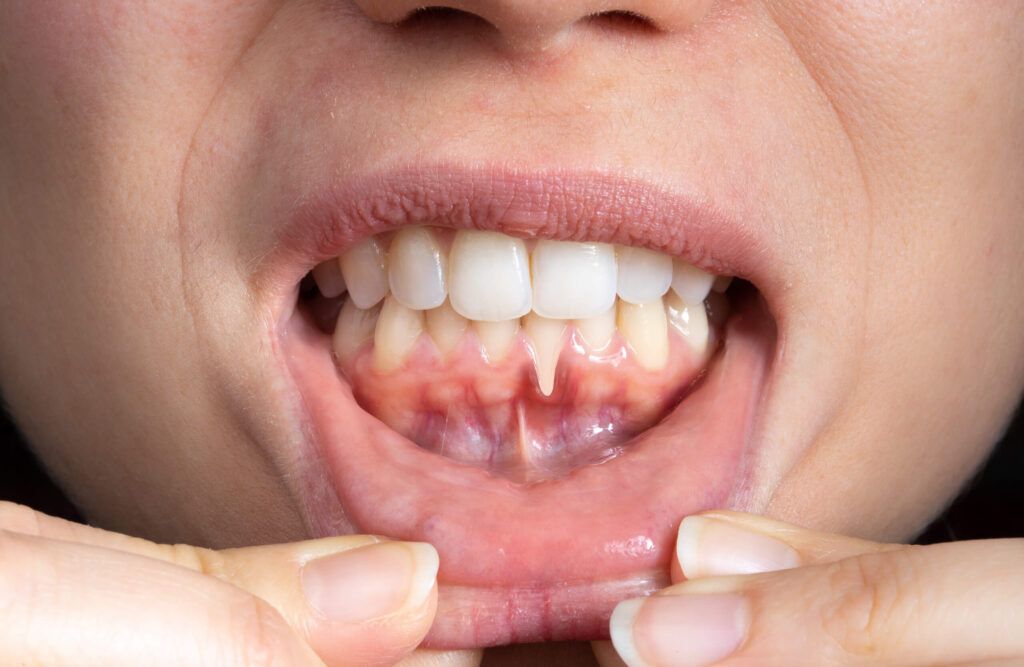
Who does gum recession affect?
While gum recession can affect people of all ages, it’s most common in people over 65 with approximately 88% having gum recession on one or more teeth. You’re more likely to develop gum recession if you:
- Have periodontal disease.
- Had braces or other orthodontic treatment.
- Have an uneven bite causing clenching and grinding of teeth.
- Use chewing tobacco.
- Have a lip or tongue piercing.
- Brush your teeth aggressively.
What are the signs and symptoms of gum recession?
The most apparent sign of gum recession is tooth root exposure. Other gum recession warning signs include:
- Pain or discomfort near your gum line
- Sensitivity to heat, cold and sweets
- Tooth sensitivity when brushing and flossing your teeth
- Tooth sensitivity during dental cleanings
- Longer appearing teeth
- Notch near the gumline
- Changes in your smile
- Spaces or gaps between teeth
- Discolored teeth around the gumline
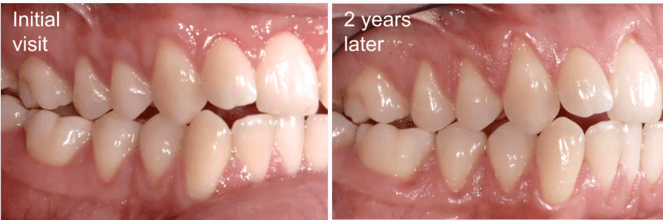
Left untreated, gum recession can lead to other serious oral health problems, such as bone loss, tooth mobility or feeling “wiggly” or even tooth loss. If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, schedule an appointment with your dentist right away.
No matter the cause of your gum recession, timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term oral health problems.
If people start treatment at an early stage, they can stop or reverse the process of gum recession. You should not ignore gum recession; if you notice these symptoms, contact Dr. Bramanti for a consultation.
What causes recession of gums?
Your gums may recede for a number of reasons. Gum recession causes include:
- Advancing periodontal disease.
- Genetics – Your genes can make you more susceptible to gum diseases.
- Brushing too hard or too aggressively.
- Dental plaque or tartar buildup.
- Hormonal changes and fluctuations in hormones that occur during a female’s lifetime
- Trauma or injury to your gum tissue.
- Abnormal tooth positioning (misalignment).
- Crooked teeth.
- An unbalanced dysfunctional bite.
- Grinding and clenching teeth.
- Diabetics have at higher risk for gum disease and increased gum recession
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Smoking or chewing tobacco use.
- Lip and tongue piercings.
What Are Receding Gums?
Gum recession is the process in which the tissue that surrounds the teeth pulls away from a tooth, exposing more of the tooth or the tooth’s root. This condition is sometimes called gingival recession. It may start to seem like your teeth are getting longer. This can cause damage to the supporting bone. Many people don’t even notice that their gums have receded because it is a gradual process. However, over time, an exposed tooth root can not only look unsightly, but can cause tooth sensitivity, especially when eating cold or hot foods. Eventually, gum recession, if not treated, can cause tooth loss. Gum recession should not be ignored as it is an indication of serious underlying gum disease and possible an unstable bite.
Consequences of Ignoring Gum Recession

Why Do Gums Recede
What causes receding gums in most people? There are a handful of reasons, including gum disease, forceful brushing, injury or teeth clenching and grinding. The surrounding bone structure may become damaged, and you may even lose some of your teeth if you do not get proper treatment. This disease can occur gradually, so you may not know you have it right away.
Gum recession is a major concern for many of our patients due to the poor esthetics and the possibility of sensitivity and decay. Studies have shown that 50% of people between 18-64 years of age have one or more sites with recession and 23.8 million people have one or more tooth surfaces with greater than or equal to 3 mm of gingival recession. It may affect one tooth or multiple teeth.
Who does gum recession affect?
While gum recession can affect people of all ages, it’s most common in people over 65 with approximately 88% having gum recession on one or more teeth. You’re more likely to develop gum recession if you:
- Have periodontal disease.
- Had braces or other orthodontic treatment.
- Have an uneven bite causing clenching and grinding of teeth.
- Use chewing tobacco.
- Have a lip or tongue piercing.
- Brush your teeth aggressively.
What are the signs and symptoms of gum recession?
The most apparent sign of gum recession is tooth root exposure. Other gum recession warning signs include:
- Pain or discomfort near your gum line
- Sensitivity to heat, cold and sweets
- Tooth sensitivity when brushing and flossing your teeth
- Tooth sensitivity during dental cleanings
- Longer appearing teeth
- Notch near the gumline
- Changes in your smile
- Spaces or gaps between teeth
- Discolored teeth around the gumline
Left untreated, gum recession can lead to other serious oral health problems, such as bone loss, tooth mobility or feeling “wiggly” or even tooth loss. If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, schedule an appointment with your dentist right away.

What causes recession of gums?
Your gums may recede for a number of reasons. Gum recession causes include:
- Advancing periodontal disease.
- Genetics – Your genes can make you more susceptible to gum diseases.
- Brushing too hard or too aggressively.
- Dental plaque or tartar buildup.
- Hormonal changes and fluctuations in hormones that occur during a female’s lifetime
- Trauma or injury to your gum tissue.
- Abnormal tooth positioning (misalignment).
- Crooked teeth.
- An unbalanced dysfunctional bite.
- Grinding and clenching teeth.
- Diabetics have at higher risk for gum disease and increased gum recession
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Smoking or chewing tobacco use.
- Lip and tongue piercings.
No matter the cause of your gum recession, timely diagnosis and treatment can help prevent long-term oral health problems.
If people start treatment at an early stage, they can stop or reverse the process of gum recession. You should not ignore gum recession; if you notice these symptoms, contact Dr. Bramanti for a consultation.
